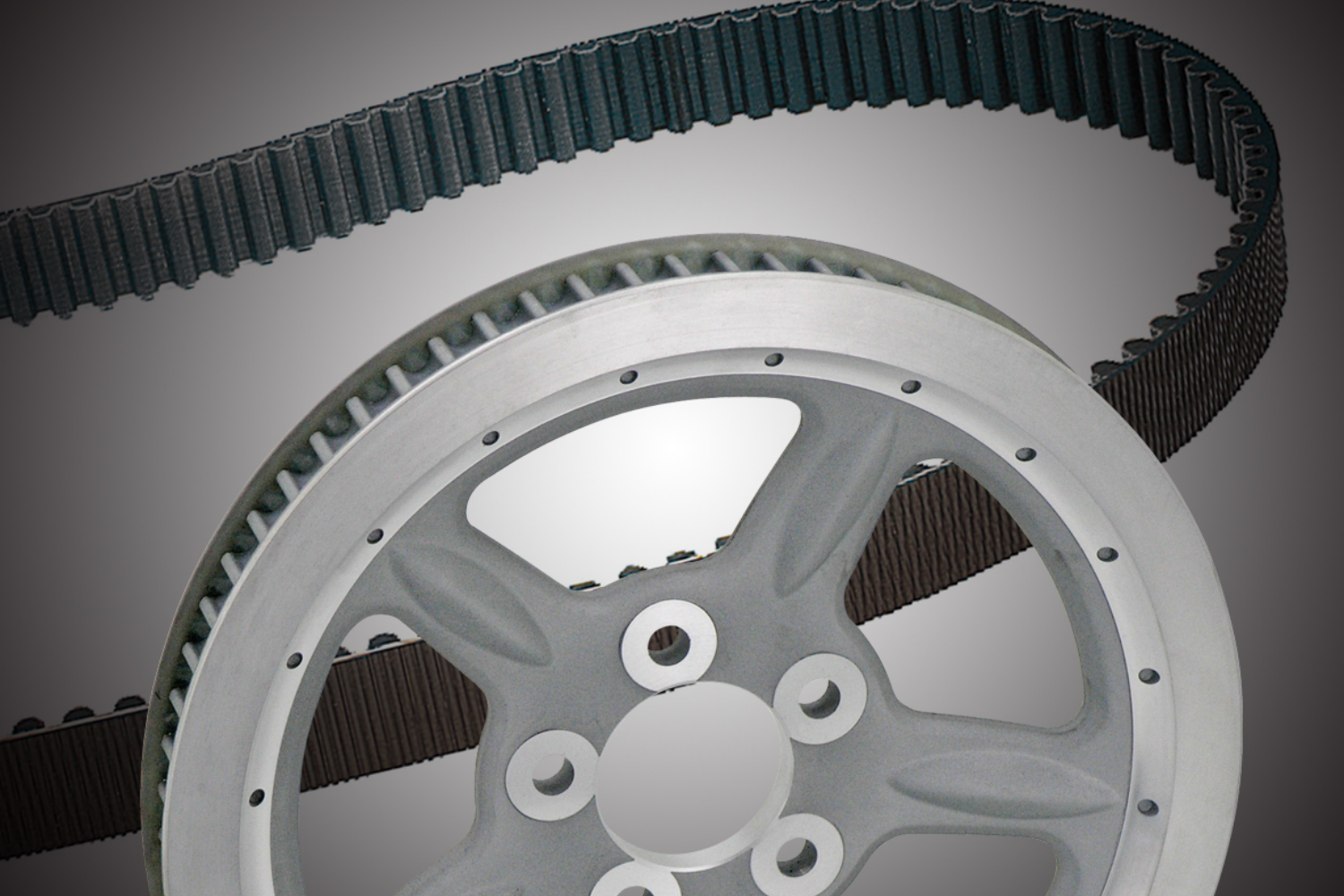
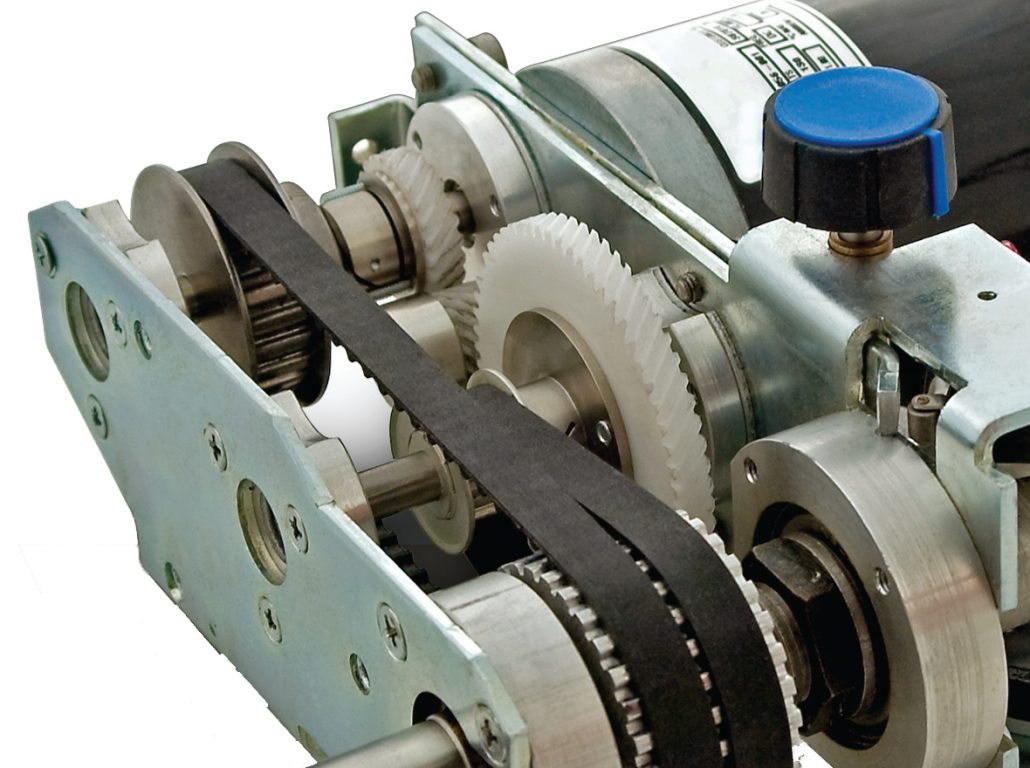
Belts and pulleys are components used in power transmission systems to transmit power from one rotating shaft to another. Belts are flexible looped components made of materials such as rubber, nylon, or polyurethane, while pulleys are cylindrical components with grooves that mate with the belts to transfer power.
Belts and pulleys are used in a variety of applications, such as in automobiles for driving accessories like the alternator and water pump, in industrial machinery for conveying materials or driving machinery, and in household appliances for driving the drum in washing machines, for example.
What types of belts and pulleys are there ?
There are many types of belts and pulleys, but some common types include:
Belts:
- V-belts: used in industrial applications for power transmission
- Timing belts: used for precise power transmission in machinery and engines
- Flat belts: used in light-duty power transmission applications
- Ribbed belts: used in automotive and industrial applications
Pulleys:
- V-belt pulleys: designed to work with V-belts and provide efficient power transmission
- Timing belt pulleys: designed to work with timing belts and provide precise power transmission
- Idler pulleys: used to change the direction of a belt or to maintain belt tension
- Flat belt pulleys: designed to work with flat belts in light-duty power transmission applications
- These are just a few examples of the many types of belts and pulleys available. The specific type of belt and pulley used will depend on the application and the requirements for power transmission.
What are the differences between different types of belts and pulleys ?
There are several types of belts and pulleys, each with their own unique characteristics and applications. The main differences between them are:
- V-belts: These have a trapezoidal cross-section and are used for high-torque, low-speed applications. They are flexible and can handle misalignment, but can slip under heavy loads.
- Timing belts: These have teeth on the inside of the belt and mesh with corresponding teeth on the pulley. They are used for high-precision applications, as they offer more accurate power transmission and are less likely to slip than V-belts.
- Flat belts: These have a rectangular cross-section and are used for low-torque, high-speed applications. They are less flexible than V-belts but can handle higher speeds.
- Round belts: These are circular in cross-section and are used for light-duty applications, such as in sewing machines. They are flexible and can handle some misalignment.
- As for pulleys, there are several types as well:
- Fixed pulleys: These have a fixed axle and simply redirect the force of the belt.
- Moveable pulleys: These have a movable axle that allows the tension on the belt to be adjusted.
- Compound pulleys: These have both fixed and moveable axles, which allows for more mechanical advantage and increased lifting power.
- Idler pulleys: These are used to redirect the belt without changing its direction of travel, or to take up slack in the belt.
The choice of belt and pulley type depends on the specific application and requirements, such as the amount of torque needed, the speed of rotation, and the precision required.
CONTINUE READING
Related Posts
In the world of industrial manufacturing, the efficiency and reliability of transmission systems are critical to the success of any […]
In industrial settings, a smooth and quiet power transmission system is crucial for productivity, safety, and worker comfort. V Belt […]
Splines play a critical role in mechanical power transmission systems, enabling rotational motion and torque transfer between mating components. These […]